Android layout is used to define the user interface for application design. A layout is a widget and UI controls that will appear on the screen of an Android application.
Generally, an application is a combination of view and viewgroup. Android application contains multiple activities. Hence, every application contains multiple user interfaces.
There are two types of Layout:
- View
- View Group
View:
A View is defined as the user interface that is used to create UI components such as ImageView, EditText, RadioButton Textview, etc.
View Group:
A ViewGroup acts as a class for layouts and holds other views or view groups to define the layout properties.
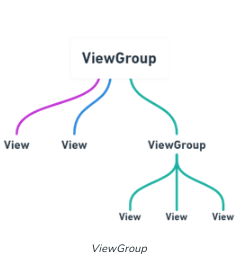
Type of Android layout
1. Android Constraint Layout:
Constraintalayout is a viewgroup subclass, specifying the position of layout constraints for every child view.
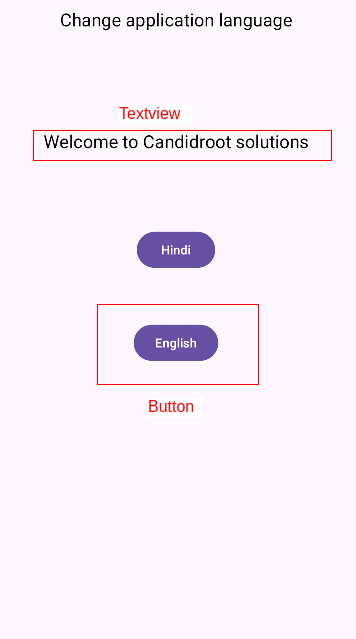
Example:
2. Android linear layout:
A linear layout is a view group, used to provide a child view set horizontally or vertically based on the orientation property.
Example:
3. Android Relative layout:
Relativelayout is a viewgroup used to specify the position of a child view.
Example:
4. Android Frame Layout:
Frame layout is a viewgroup, used to specify the position of the child view.
Example:
5. Android Table Layout:
Frame layout is a viewgroup, used to specify the position of child view elements in rows and columns.
Example:
6. Android Grid view:
Grid layout is a viewgroup, used to specify the position of the child view display.
Example:
Happy Coding.